A Technical Perspective on Powder Compressibility in the Pharmaceutical Industry
The Carr Index (also known as Carr’s Compressibility Index) is a widely utilized parameter in the pharmaceutical industry to evaluate the flow properties of powders. Named after the eminent scientist Ralph J. Carr, Jr., this index provides a quantitative measure of a powder’s compressibility, a critical factor in formulation and manufacturing processes.
Calculating the Carr Index
The Carr Index is derived from the relationship between two key density measurements of a powder:
- Bulk Density (ρB): The density of the powder when loosely packed.
- Tapped Density (ρT): The density after the powder has been compacted by tapping.
The formula for calculating the Carr Index is expressed as:
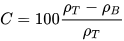
Alternatively, it can also be represented as:
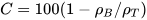
Here, ρB is the bulk density, and ρT is the tapped density.
Significance in Powder Flowability
The Carr Index is an invaluable tool in pharmaceutics for predicting powder behavior during processes such as blending, granulation, and tableting. Powders with low Carr Index values (typically less than 15%) exhibit good flow properties, making them ideal for high-throughput manufacturing environments. Conversely, powders with high Carr Index values (greater than 25%) indicate poor flowability, which can lead to challenges such as segregation, uneven feeding, or inconsistent tablet weights.
This relationship is rooted in the understanding that free-flowing powders show minimal differences between bulk and tapped densities due to reduced interparticle interactions. On the other hand, poor-flowing powders exhibit significant density changes, reflecting higher interparticle friction and cohesion.
Comparing the Carr Index and Hausner Ratio
Another complementary metric for assessing powder flowability is the Hausner Ratio, defined as the ratio of tapped density to bulk density
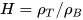
Both the Carr Index and Hausner Ratio are empirical methods. While their theoretical underpinnings may not be robustly established, their practical utility in pharmaceutical applications is undeniable. They provide quick and cost-effective insights into powder properties, requiring minimal equipment and expertise.
Practical Implications
Despite some criticism regarding the lack of a strong theoretical basis, the Carr Index and Hausner Ratio remain indispensable in the pharmaceutical industry. These tools enable scientists and engineers to anticipate challenges in powder handling and optimize formulations for manufacturability. Their simplicity, coupled with the ease of measurement, makes them essential for quality control and R&D workflows.
Industry Standards for Flowability
- Carr Index < 15%: Indicative of good flowability.
- Carr Index > 25%: Suggestive of poor flowability.
By employing these indices, formulators can make informed decisions about powder modifications, such as granulation or excipient addition, to achieve desired processing characteristics.
The Carr Index, along with its counterpart the Hausner Ratio, continues to be a cornerstone in pharmaceutical powder characterization. Its adoption underscores the industry’s reliance on practical, efficient, and accessible tools to ensure product consistency and manufacturing excellence.
Reference source –






